Pupil Size and Pupil Dilation Velocity: What They Mean in Neurology
Pupil dilation velocity is essential for evaluating the percent change in pupil size and the neurological status of individual patients. This blog helps understand and enhance the knowledge of pupil dilation velocity and its importance in neurology.
What is a traumatic brain injury?
Traumatic brain injury (TBI) is the leading cause of death and disability in children, teens, and young adults, accounting for 20% of all deaths.
TBI refers to a wide range of injuries that can occur. When there’s sudden damage or trauma to a patient’s brain. Forces, such as a hard blow or jolt to the head that causes. Your brain to move back and forth within your skull, cause traumatic brain injuries. This can cause bleeding inside the patient’s skull, bruising on the brain’s surface, or both.
Other potential causes include penetrating wounds like gunshot wounds or being hit by a fast-moving object like an automobile.
Depending on what part(s) of the patient’s brain was injured and how severe it was, they may experience short-term symptoms like confusion or difficulty walking right after sustaining a TBI or long-term complications such as headaches, memory loss, anxiety disorders such as PTSD, depression, etc.
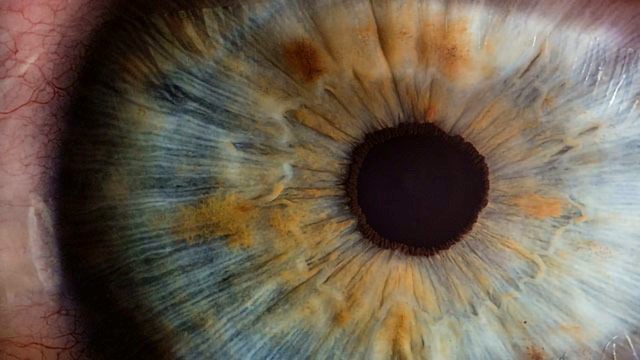
What is pupil size evaluation?
The pupil size of the eye is a neurologically based sign.
If a doctor sees that someone’s pupils are larger than normal, that indicates brain damage or injury. If they see that someone’s pupils don’t respond in the way they normally do to light, this can be a sign of brain trauma or some other neurological disorder. Pupil evaluation is something that happens routinely in emergency rooms and intensive care units.
A patient who has had an episode where their pupils were abnormally dilated, such as from a traumatic brain injury or seizure—and then “pupillary constriction” does not occur when light is shined into their eyes, may need to be evaluated for possible damage inside their head and other neurological issues.
What does the change in pupil size tell doctors about brain injury?
A change in pupil size can be an indicator of brain injury, whether mild or severe.
It’s important to note that the pupils are much more responsive to injury than any other body part. For example, a person who gets hurt in their arm might feel pain in that area, but they’ll likely only notice it when they look down at their arm and see blood or bruising. In comparison, someone with a brain injury may have no symptoms until their pupils dilate (or constrict) because of sudden changes in pressure within their skull.
This is because the brainstem controls all autonomic functions like pupillary functions, blood pressure regulation, and heart rate.
Therefore, changes in someone’s central nervous system will be reflect first by changes in these autonomic reflexes before any symptoms arise from higher-level thinking centers like memory loss or confusion.
Why is pupil dilation velocity important in neurology?
Pupil dilation velocity measures the speed at which the patient’s pupils dilate.
This can give doctors and researchers an idea of how well the patient’s brain is functioning. And identify potential issues in the brain. For example, dilation velocity may be use to determine whether the person has damage. To their retina or optic nerve because of traumatic brain injury or disease, such as multiple sclerosis.
Pupil size is an important indicator of neurologic health because it’s control by the parasympathetic nervous system, which controls “resting” functions such as breathing and digestion.
When these systems aren’t working properly. They’ll cause changes in pupil size that can be measure using a device called a pupilometer.
What is the role of the pupilometer in the evaluation of pupil dilation velocity for people with TBIs?
A pupilometer is a tool use to measure the dilation velocity of the pupils.
Health professionals often use it to diagnose traumatic brain injury (TBI), concussion. And other conditions that may cause dilation, like Horner’s syndrome. When a doctor uses a pupilometer to look into someone’s eyes. They can tell if they have a brain injury because their eyes will be dilate or not. The pupilometer is a tool use to measure how much time it takes for their pupils to get back to normal size after the clinician shines a bright light on their eyes.
If the person has a concussion or TBI, their eyes might not return to normal size as quickly as they should.
What makes the pupilometer better than other neurological tools?
The pupilometer is a non-invasive, portable, and cost-effective tool that health experts can use to assess the health of the brain and nervous system.
It is safe and quick, requiring only a few seconds per patient. Additionally, it can provide valuable information about pupillary reflexes with no additional training—allowing. The professional to interpret them immediately, even if they don’t have any knowledge of neurology or neurosurgery. NeurOptics has designed the pupilometer with durability in mind; its durable makeup will keep it in good condition for many years.
For this reason alone, it may be worth investing in one for your practice as a better method for testing pupil dilation velocity (PDV).